As much as necessary, as little as possible - thanks to predictive maintenance
By linking, visualizing and analyzing digital data, new methods are available to operate and maintain machines and plants much more efficiently than before. With predictive maintenance, you always act at the right moment and only maintain machines and plants when it is really necessary.
Through continuous measurement and evaluation of machine data:
- identify possible wear or deviations of the equipment in the production process
- increase production reliability and the efficiency of maintenance measures
- maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
This allows you to better plan downtime and minimize unplanned downtime.
The advantages and disadvantages of different types of maintenance
Machine maintenance is an integral part of every manufacturing company. Often, companies only react to the behavior of their machines and systems: If a defect occurs, the machine is at a standstill until the defect is eliminated. However, it is more time and cost-saving to plan maintenance on the basis of data. This allows you to intervene before the machine comes to a standstill and also to optimize the mean time to repair (MTTR) in the long term. We introduce you to the advantages and disadvantages of common maintenance approaches in more detail.
![]()
Reactive
Maintenance
Machines and systems are operated without insight into data and conditions until maintenance is required. Maintenance occurs when the damage occurs.
Advantages:
- plant can be operated up to maximum production output
- no further investments are necessary for data acquisition and co.
Disadvantages:
- costs for repairs can significantly exceed production value
- long, unplannable downtimes occur
- the damage can have stray effects on other machine parts
- usually only symptoms are repaired, not the causes
- high financial burden
![]()
Preventive
Maintenance
In preventive maintenance, machines and systems are serviced according to a fixed schedule. Historical data and empirical values often serve as a basis.
Advantages:
- extended service life of the plant
- real failures can be avoided
- cost savings possible compared to reactive maintenance
Disadvantages:
- machine parts with remaining service life are replaced
- even running machines without risk of failure are taken off the line - unnecessary downtimes are caused
- possibly worn parts are not taken into account
- unplanned downtime still possible
- comparatively high costs
![]()
Condition-based
Maintenance
Condition-based maintenance makes use of a range of machine, process as well as historical data to report abnormalities and malfunctions in operation.
Advantages:
- maintenance before a failure occurs, but only when needed
- reduction of downtime
- efficient and cost-saving spare parts management
- captured data can also be used for other use cases
Disadvantages:
- maintenance times cannot be planned or predicted
- machines must be made fit for data acquisition
- initial costs
![]()
Predictive
Maintenance
Here, based on recorded operating and process data as well as the actual condition of the machine, a prediction is made as to when the machine or system needs maintenance.
Advantages:
- maintenance can be planned
- downtimes are reduced to a minimum
- service life of machine and parts is increased
- personnel deployment and spare parts can be planned precisely
- high cost savings possible
Disadvantages:
- machines must be made fit for data acquisition
- initial costs
![]()
Prescriptive
Maintenance
With this technology, the system not only predicts failures, but also provides the recommended measures. Even independent initiation of measures can be implemented.
Advantages:
- high time savings due to self-learning automatisms
- minimum downtimes
- maximization of service life and uptime
- service technicians do not have to determine troubleshooting measures themselves
- support through analytics tools
Disadvantages:
- high initial outlay for software and equipment
- very complex to implement
4 Milestones on the Way to Successful Predictive Maintenance
The road to effective predictive maintenance is certainly no walk in the park. Your specific goals, the existing, usually heterogeneous machinery and complex production processes place high demands on the implementation strategy. But the effort is worth it, because with predictive maintenance you can influence your production performance significantly and sustainably. There are 4 points you should keep in mind during implementation:

Creating a
data basis
The right data foundation is the basis for your journey towards predictive maintenance. To create this, you need to know at what stage of maturity you are. Depending on how far your machines are digitalized, different and more detailed data will be available to you. Keep in mind that not only production is relevant. Other areas such as product management, IT and maintenance should also influence this database.

Setting the
right focus
Machine data, process data, environmental data from your production: In order to effectively predict unplanned downtime, you need to know what information you want to gain from the collected data. Define the targeted insights as clearly as possible, since only then can you avoid spending a lot of time collecting the data. Collect and process exactly the data that is important for your predictive maintenance.

Transparency &
visualization
Once you have created the data basis and defined the insight targets, the next step is to make your data readable. Up to this point, the data from your machines and plant only runs on your server or in the cloud. With targeted visualizations, you create transparency in your processes and enable threshold and trend analyses. Initial optimizations can already be achieved at this point by manually comparing the ACTUAL data with the TARGET values.

Recognizing
correlations
Up to this point, sensors, gateways and software have done their job. Now it's up to you to correlate the collected data and identify context. Evaluate historical machine data in an automated way and find causes for previous failures or anomalies. This enables you to derive patterns that you can project onto current and predicted machine behavior. Analytics tools support you in this.
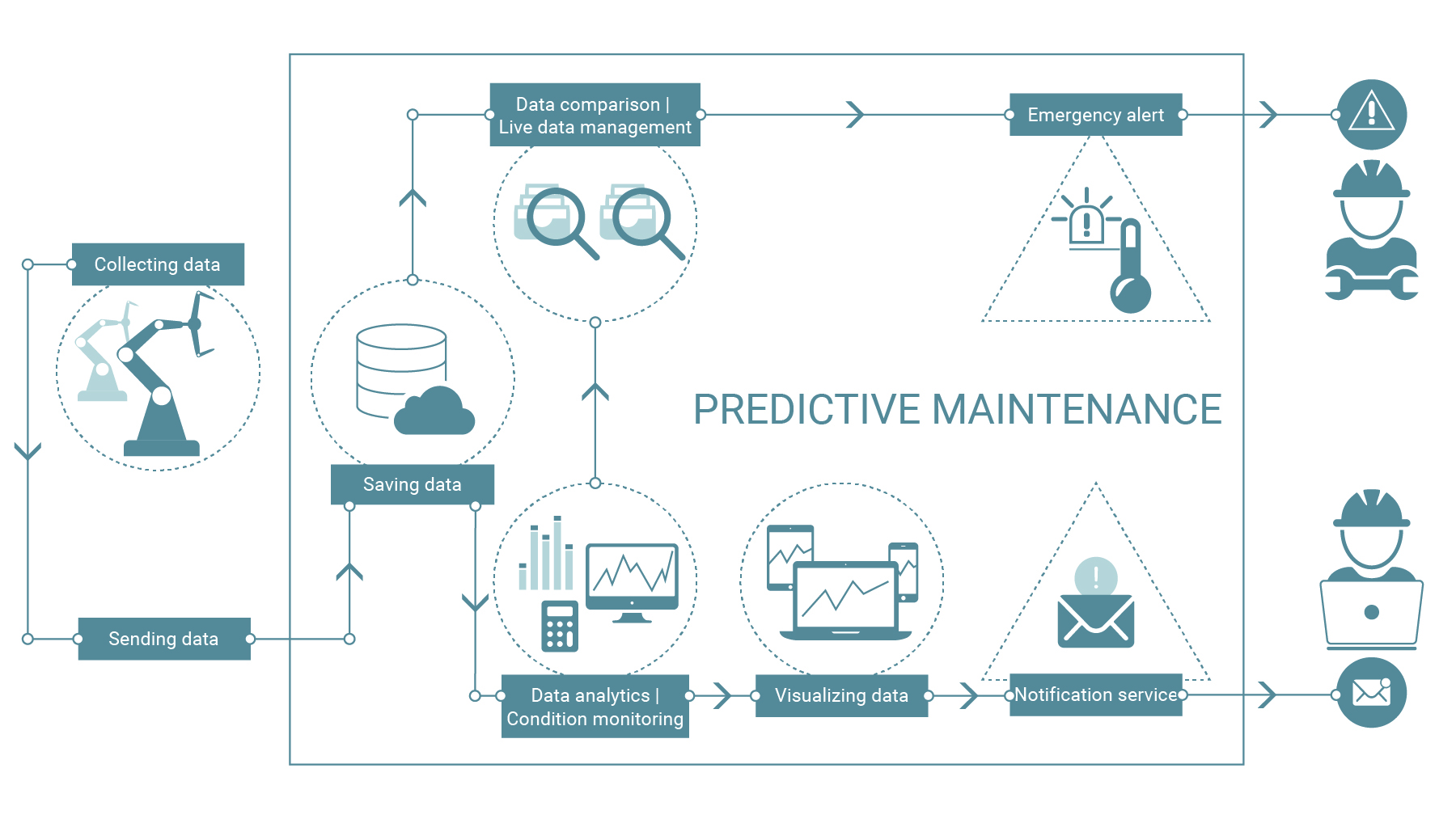
Predictive maintenance for the maintenance of machines & plants

The greatest goal of maintenance in a manufacturing company is to intervene as little as possible in production and to keep machine availability as high as possible. Unplanned downtimes should be kept to a minimum. To achieve this, data is generated and processed automatically. The result: a real-time overview of the machine status, alarming when certain target values approach a critical range, and an overview of reasons for downtime that have occurred. This allows you to plan the ideal time for maintenance and repair, avoid unplanned downtime, and reduce costs.
You improve your overall plant effectiveness by:
- higher availability of your machines/plants
- longer service life of your machines/plants
- higher process and operational reliability
- reduction of unplanned downtimes
You reduce your costs because you:
- can plan maintenance cycles better
- reduce expenses for repairs and spare parts
- have less coordination effort with service providers
- avoid downtime - nothing is as expensive as an hour of unplanned production downtime
Frequently asked questions about predictive maintenance
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a maintenance strategy designed to identify potential problems in machinery and equipment before they lead to downtime. By monitoring and analyzing machine data, deviations and anomalies can be detected and predictive models can be developed to:
- determine the optimal time for maintenance and repair
- minimize costly downtime
- extend the service life of machines.
How much does predictive maintenance require?
Predictive maintenance requires a combination of several components:
- data acquisition systems to collect machine and plant data
- analytical tools /algorithms for data processing and pattern/anomaly detection
- predictive models to forecast the optimal maintenance time
- a suitable infrastructure for storing, processing and analyzing large amounts of data
- trained staff to analyze data and interpret and implement maintenance and repair plans
When does predictive maintenance pay off?
Predictive maintenance is particularly worthwhile in the following cases:
- for machines and systems that are critical for production or safety
- when you incur particularly high costs due to unplanned downtime and repairs
- when spare parts or qualified maintenance personnel are difficult to obtain
- if you define maintenance intervals only according to the manufacturer's specifications or calendar instead of actual requirements
Why is predictive maintenance important?
Predictive maintenance is important because it can reduce unplanned downtime and repairs. Monitoring machine data makes it possible to identify causes of failure at an early stage and to initiate maintenance or repair measures. This improves the efficiency of maintenance processes, reduces costs and increases the availability of machines and systems, which in turn has a positive effect on productivity and value creation.
