Definition: What does process stability mean?
Process stability is a concept from quality management that describes the ability of a manufacturing process to continuously produce within defined tolerance limits.
A stable manufacturing process has the following characteristics:
- There are no unexpected fluctuations or outliers.
- All influencing variables are consistently under control.
- The measurement data shows a constant position (average) and dispersion (fluctuation).
- The results of the process are reproducible and reliably predictable.
Requirements for process stability
In order to turn a process into a stable process, a number of prerequisites must be met. And these prerequisites must be created in various parts of your production - depending on the respective process, your industry and, last but not least, your specific goals. For example, the following prerequisites may be involved:
- the use of standardized operating procedures (SOP) to ensure uniform processes
- the binding specification of validated process parameters for process control
- the involvement of qualified personnel with appropriate training and experience
- systematic documentation of all setup processes and setup times
- the integration of modern technologies to support and monitor processes
Summary:
- standardize procedures through SOPs and validated process parameters
- deploy qualified, trained personnel with clear responsibilities
- use modern systems for process monitoring and seamless recording
Advantages of process stability
Stable processes with a reliable, clear output are a key component of your competitiveness. They make your production easy to plan and ensure a high degree of reliability. You always know which resources you need and can use them efficiently.
Fluctuations in the process are quickly visible so that you can immediately tackle the causes. In the best-case scenario and with optimum process stability, these fluctuations will be within a predefined range anyway. This not only eliminates the need for root cause analysis. Stable processes also ensure that you avoid quality problems and guarantee consistent results. And in the end, this is reflected in your costs: you save time and money thanks to fewer rejects and less rework.
Last but not least, of course, your customers also benefit: you produce highly reliably, can meet deadlines and your budget and ultimately ensure a high level of customer satisfaction.
Summary:
- clear processes enable planning, reliable use of resources and time savings
- fewer fluctuations mean fewer rejects, consistent results and higher quality
- adherence to deadlines and reliable product quality increase customer satisfaction
Establish & monitor process stability
In order to establish process stability, you first need to listen to your processes. What happens and how? What goals are your processes working towards? Within what limits do they operate and within what limits should they operate? Process stability is initially a definitional framework in which you determine when a process is stable.
Once the framework has been set and the necessary prerequisites have been created, the next step is to monitor process stability. Nothing works here without process data, which you must of course record over a defined period of time.
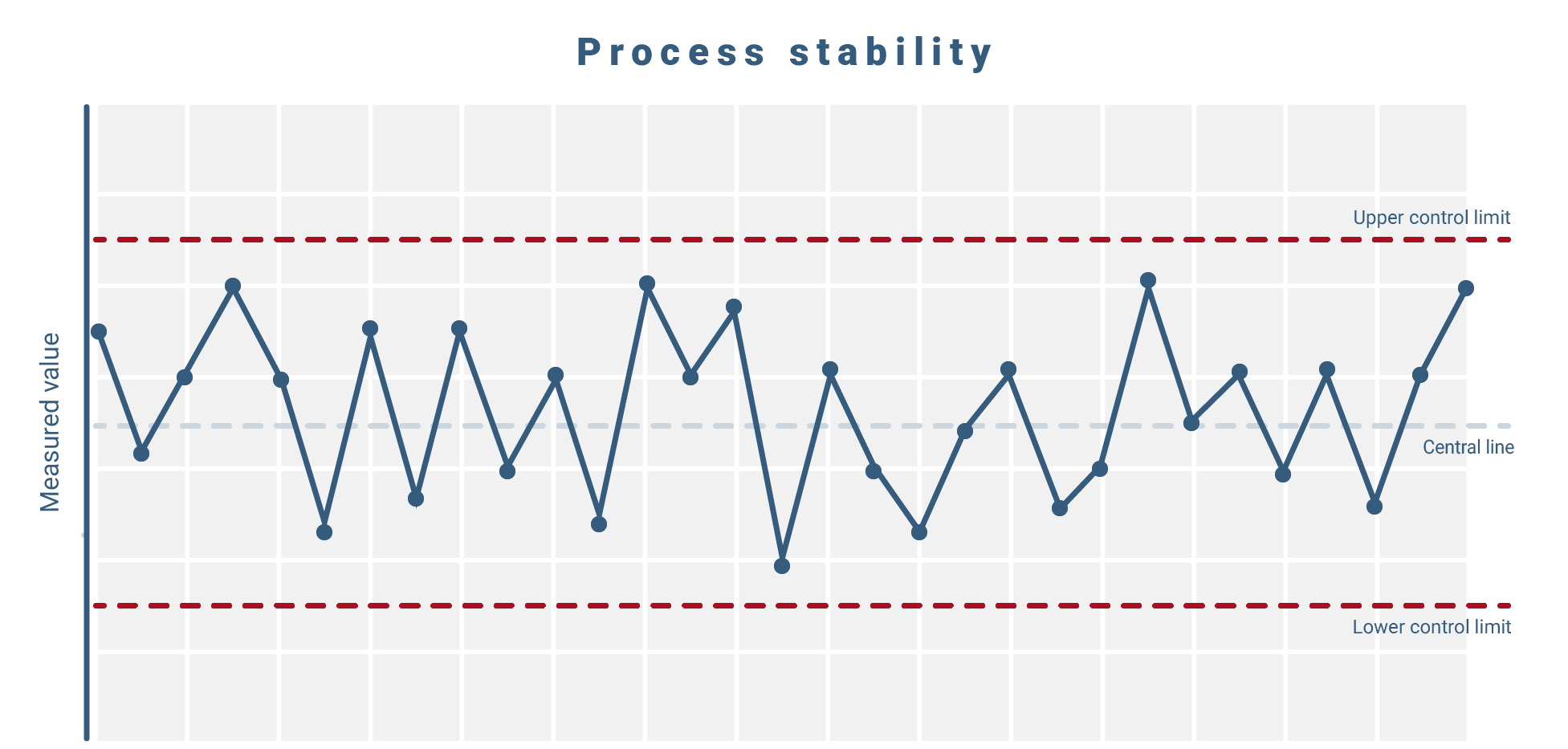
Prepare the data in the form of control charts (in the sense of statistical process control or SPC) in order to monitor processes analytically and identify trends, outliers and patterns.
You can also analyze scatter and position based on the recorded data. You can evaluate mean values and fluctuation ranges and derive an assessment of process stability from this.
If you determine that instabilities are occurring in your process, you can use the recorded data to analyze the causes. Use methods such as the Ishikawa diagram (fishbone diagram) or the 5 Why method to identify and eliminate sources of disruption. This in turn contributes to greater stability in your processes.
Summary:
- define framework: Analyze processes, define stability criteria and limit values
- systematic collection of process data for monitoring
- use control charts (SPC) for analytical monitoring of trends, outliers and patterns
- analyze mean values and fluctuation ranges to assess process stability
- identify and eliminate sources of interference using established methods
What are your goals with process stability?
In the end, it's always about competitiveness, isn't it? Well, yes, it really is and process stability can also be a suitable means of keeping you competitive in the long term.
When you establish stable processes, you are aiming for targeted process optimization to increase efficiency, quality and stability in your production. Thanks to the predefined process framework and the set limits, you can identify weak points and deviations from the optimum process at an early stage and eliminate them immediately.
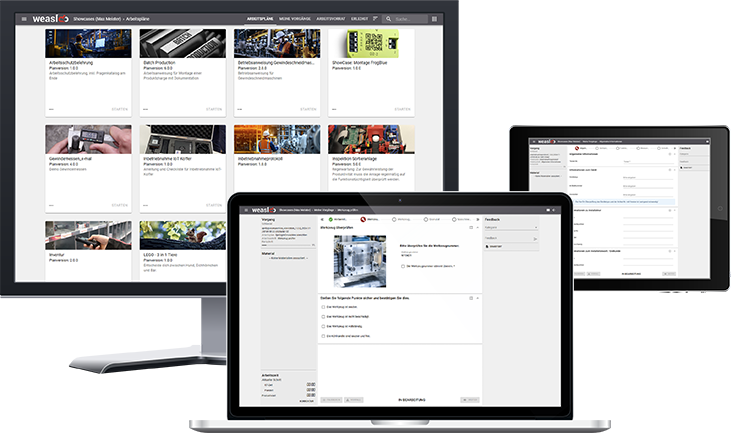
The ideal assistant for stable processes
With standardized work instructions, predefined parameters and qualification-oriented information, you create the conditions for stable processes. In other words: with weasl you can establish process stability in your production.
Sounds appealing? Then take a look at what weasl can do - in our free showcase environment.