APQP: Definition & meaning
APQP is a systematic process for the early quality planning of products. Before the actual production phase - i.e. during the design and development process - measures are defined to ensure the desired product quality.
This quality management tool has its origins in the QS 9000 standard and its successor standard IATF 16949, both of which originate from the automotive industry, but this does not mean that APQP cannot also be used in medical technology, mechanical engineering or other industries.
APQP stands for Advanced Product Quality Planning.
Summary:
- APQP = systematic advance quality planning before the start of production
- riginated in the automotive industry, today applicable across all industries
- objective: to ensure product quality through early measures
Prerequisite for APQP
The most important prerequisite for effective Advanced Product Quality Planning is cross-departmental cooperation. In order to plan for high product quality in advance, you need to bring the development department, production, quality assurance and supplier management together. The departments then work together to derive measures and options.
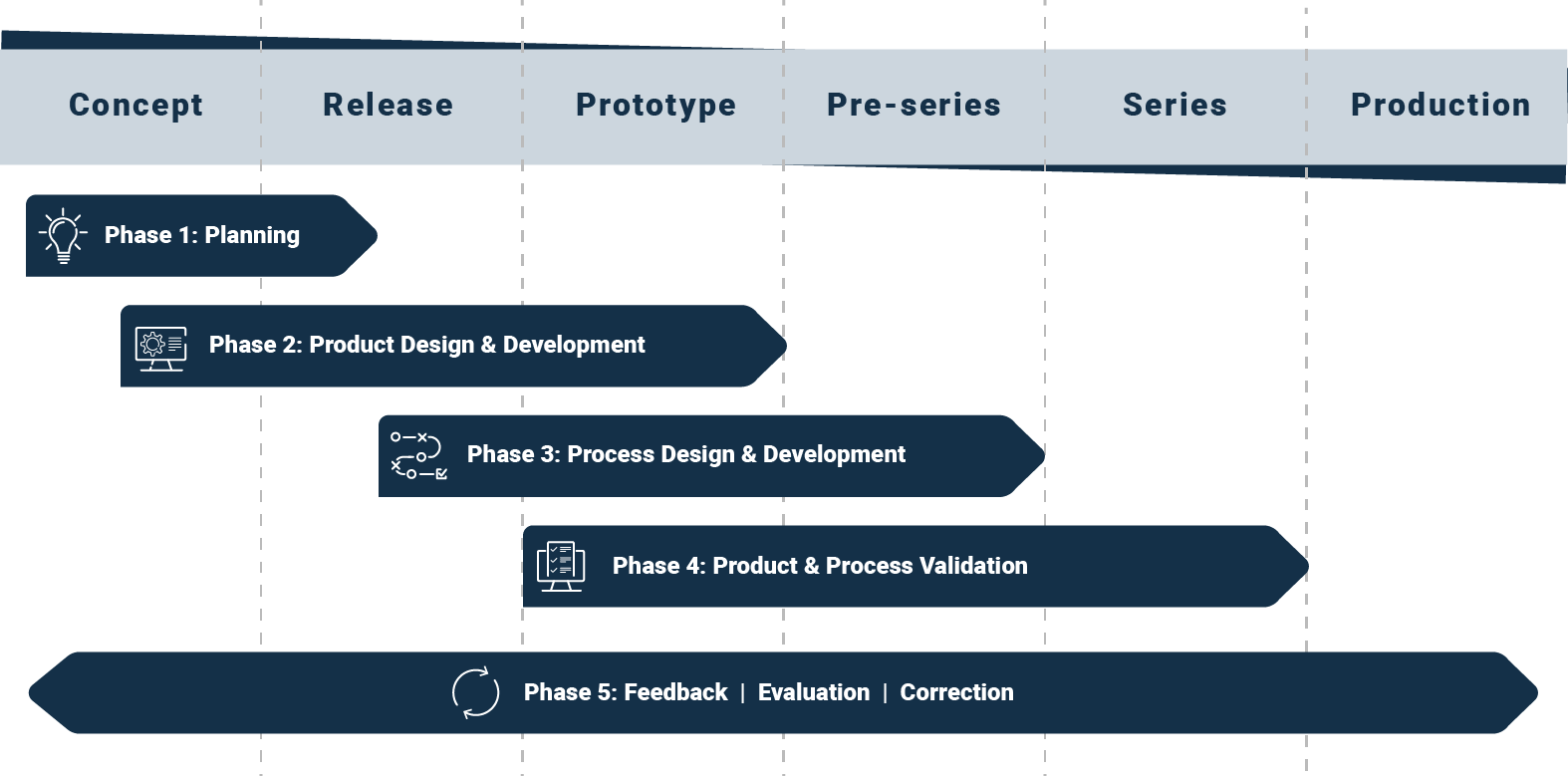
The 5 phases of the APQP project structure
APQP processes must be carefully planned in order to achieve the desired result. And they may need to be redefined for each new assignment. The best way to do this is to use the 5 phases of the APQP project structure as a guide.
Phase 1: Planning & conception
That's to do:
Record all customer requirements and expectations as fully and completely as possible. Clarify the project requirements and framework conditions.
That's the result:
Typically, at the end of this phase you will have specifications and concrete quality and reliability targets.
Phase 2: Product design & development
That's to do:
In this phase, the responsible departments develop a product design that is suitable for series production. You also plan all assembly and production processes.
That's the result:
At the end of this phase, you have a failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) for the design and the final product. You have created a prototype and drawn up a production control plan.
Phase 3: Process design & development
That's to do:
You know what needs to be produced. Now it's all about the “how”. In phase 3, you work out efficient production processes and select the appropriate equipment, machines and systems.
That's the result:
You conclude phase 3 with a concrete process flow chart and a process FMEA.
Phase 4: Product & process validation
That's to do:
In this step, you validate that all theoretical and prototypical preliminary work can withstand the reality of production. In other words, you ensure that the production processes deliver reproducible products according to customer specifications.
That's the result:
Typically, at the end of this phase, you will have clear reports on the success or failure of your measures. These may include
- test equipment capability analyses,
- sampling in accordance with PPAP (Production Part Approval Process)
- initial sample test reports
Phase 5: Feedback, evaluation, correction
That's to do:
You have now established an APQP process and must collect feedback on it and continuously reassess the process steps. You keep your eyes open for deviations and initiate corrective measures where necessary.
That's the result:
Over time, you optimize and stabilize the established processes more and more. Statistical process control (SPC), for example, helps you to do this.
Another important tip: document all phases of an APQP project systematically in a status report and evaluate each phase separately before starting the next phase. This will help you to identify any need for action and avoid “follow-up errors” in later phases.
Summary:
- Phase 1: clarify customer requirements and define quality targets
- Phase 2: develop product design suitable for series production, create prototype
- Phase 3: plan production processes and create process FMEA
- Phase 4: validate product and processes under real conditions
- Phase 5: evaluate feedback and optimize processes
- Important: document and evaluate each phase separately in order to detect errors at an early stage.
Advantages of APQP
Admittedly, APQP requires you to invest a considerable amount of time and “brainpower” in your production processes in advance. But the effort can be well worth it. Advanced Product Quality Planning helps you
- identify and eliminate potential sources of error at an early stage
- actively avoid errors instead of reworking them
- establish targeted measures to avoid quality defects in series production
- introduce structured planning and control processes to ensure compliance with defined quality requirements
- continuously develop and optimize product quality
- ensure that your products meet customer requirements and expectations
- increase customer satisfaction
Summary:
- early error prevention through structured planning
- sustainable quality assurance also in series production
- higher customer satisfaction through targeted measures
Goals of APQP
Let's keep it short: the overarching aim of APQP is to identify all the necessary steps and measures required for a high-quality end product before production begins. This enables lean, error-free production processes and a high level of customer satisfaction.
Set new quality standards – with digital processes in weasl
Support your APQP processes by empowering your employees to work error-free at all times. Digital work instructions in weasl make it possible - and also provide you with essential insights into optimization potential.
Take a look for yourself - in our showcase environment.