Definition: What is a media discontinuity?
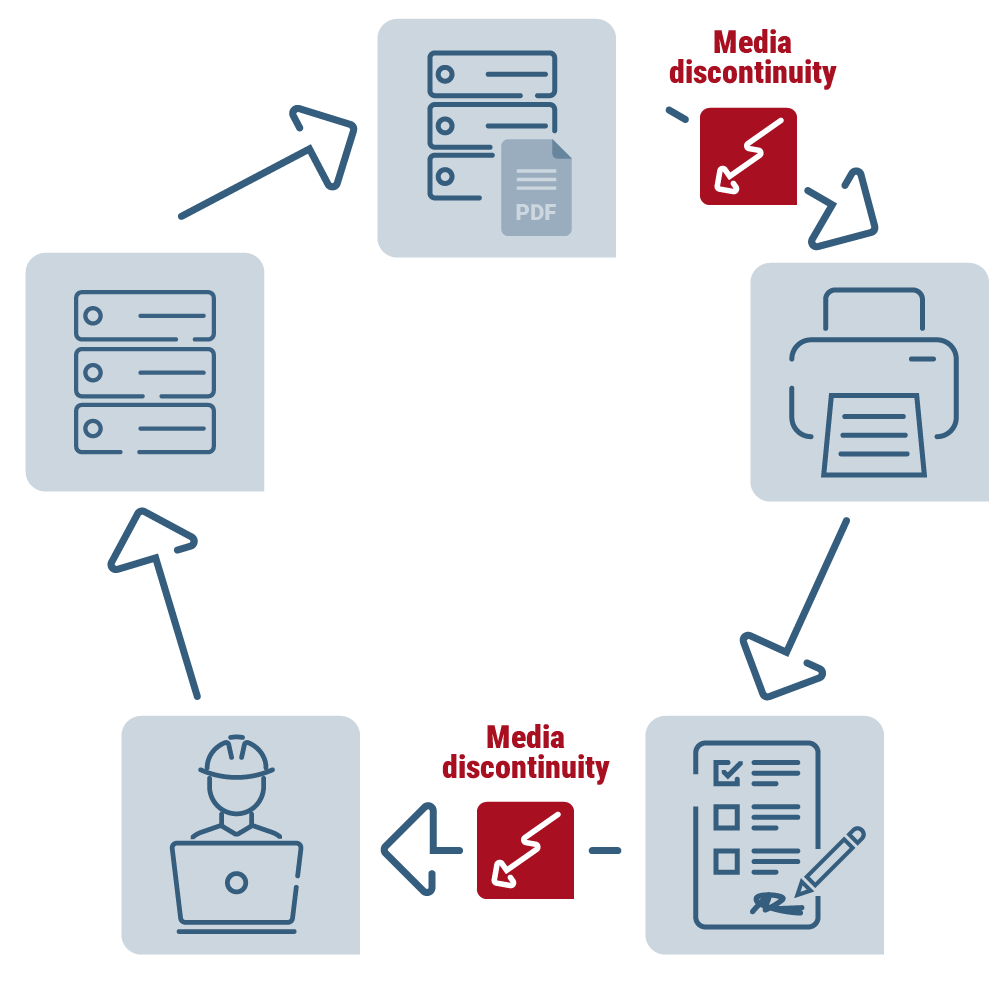
A media discontinuity always occurs when data and information are or have to be transferred from one medium to another within an information transfer chain.
An example could look like this: You receive a call with relevant information. You write this information in an e-mail and send it on to a colleague. The colleague then transfers the information to a CRM system.
In this example, there are two media discontinuities, one when the verbal content is written down and one when it is transferred from an email to another system.
What are the problems and disadvantages of media discontinuities?
Media discontinuities are disruptions in the information chain and as such inevitably brings with it a number of disadvantages and problems.
Process-related problems
Our example above illustrates this very well: whenever a media discontinuity has become part of a process, it is a sure sign of unstructured and inefficient workflows. The individual media along a transmission chain are not consistently integrated, resulting in longer processing times. This in turn causes problems with data procurement and processing - not to mention the lack of transparency regarding workflows and data flows.
Problems with data quality
Imagine you have to manually transfer the manual transcript of a call into a digital system. There are already at least two sources of transmission errors in this process. Every media discontinuity increases the susceptibility to errors during data transfer. As a result, the quality of the data and information suffers and there is a considerable risk of data loss or corruption.
Data storage & compliance
Data stored on different media or at different storage locations not only causes duplicate data storage. It can also lead to data records with different levels of up-to-dateness. This in turn can have an impact on your compliance - especially when it comes to sensitive data. Potential security and compliance breaches are a real risk.
Summary:
- inefficient processes due to lack of integration and long processing times
- low data quality due to increased susceptibility to errors during manual transfer
- compliance problems due to duplicate, distributed and outdated data storage
Examples of media discontinuities
Putting a conversation on paper is certainly one of the most obvious media discontinuities. However, they also occur in places where you might not even think of a media discontinuity at first. But let's start with the obvious:
From analog to digital
When analog and digital processes come together, this usually means that Information is first recorded on paper and then manually transferred to a digital system. A not so unusual example can be found in everyday production.
Imagine you receive an order digitally. Medium 1 is the digital carrier. You then print out the order and the relevant instructions for production. Here we have the first media discontinuity. Your workers work with the paper and document manually on the paper during production. The documented data is then manually transferred back into a digital system - media discontinuity number 2.
From digital to digital
Media discontinuities also occur when data is transferred between different software applications. This always happens when the systems are not connected to each other and cannot exchange data automatically. Manual transfer is then always necessary.
An example: You need certain customer data in your project management tool and in the accounting software. So you start your CRM and transfer it manually to the target systems.
From external to internal and vice versa
Media discontinuities also occur when you exchange data with third parties - for example suppliers or partners. With media discontinuity, this means that if the systems are not coordinated with each other, data is once again transferred manually. Without media discontinuity, on the other hand, the systems convert the respective data and ensure compatibility between the systems.
Summary:
- analog to digital: paper-based information must be manually transferred to the system
- digital to digital: manual intermediate steps for data transfer between non-linked software
- external to internal: incompatible systems at partners/suppliers lead to manual data transfer
How can you avoid media discontinuities?
If you want to banish all media discontinuities from your company, then you may have a bit of work ahead of you. As you have seen, switching from analog to digital is not enough. The systems must be coordinated and integrated with each other. If you want to effectively avoid media discontinuities, you should:
- standardize processes to achieve a unification of workflows
- introduce clear guidelines and procedures for recording, processing and transferring information
- increase your company's level of digitalization by replacing analogue processes with suitable software
- create consistent information flows
- seamlessly integrate new systems into the existing IT system landscape
- establish automated workflows and data transfers to reduce manual intervention
- train your employees in the use of the software used and the defined processes
Summary:
- integrating processes and systems: standardized workflows and seamless IT links avoid media discontinuities
- drive digitalization: replace analogue steps with suitable software and automated workflows
- involve employees: Training ensures correct use of systems and compliance with processes
Eliminate media discontinuities from your production
Imagine if your employees in production and assembly were supported digitally throughout - from order processing to documentation, without any media discontinuities and with the certainty of delivering the best possible results. A clear case for our weasl worker guidance system.
Experience what weasl can do for your production: Book your free access to our showcase environment.